FMEA - What is it?
Risk management
If we think of risk as an uncertain situation, condition or event that involves exposure to danger, loss, harm, injury or any other threat, risk management is the tool to avoid occurrence or to minimize the consequences if the risk occurs and the negative effects appear.


Failure mode and effect analysis
How expensive can be a failure? Are all risks avoidable? Which consequences can a failure cause? Why are there failures?
The FMEA is a risk management technique, a great one. The american army started using it back in the 1950’s. The NASA adopted it in the 1960’s. The automotive industry adopted it in the 1970’s-80’s.
A failure can be expensive but, how much? It will depend on the context, product type, its functions, failure mode, etc.
I wrote 2 articles about risk, you might want to take a look as well: Risk-based thinking and risk management.
In this post we will focus on the fmea as “quality core tool” for the automotive industry.
The FMEA is not only a great risk management technique but it is as well one of the requirements called in the standards of the quality management like ISO9001 and IATF16949. It is also a customer requirement.
FMEA and safety
As we mentioned before, the FMEA is required by customers and quality standards. The official guideline for the FMEA in the automotive industry is the manual prepared by the AIAG and the VDA and published in 2019. In the manual you will find the principles, the 7-step method to make the design and process FMEA’s and the corresponding evaluation tables.
First of all, I would like to stress that one of the main concerns in the automotive industry is SAFETY. Some of the risks or FAILURE MODES can have an impact on safety and therefore be related to product liability. In the FMEA handbook you will find at the beginning some explanations of the legal importance and impact of the FMEA and the obligations to fulfill when preparing it.
I strongly suggest using the manual and reviewing your customer requirements when preparing your FMEA’s.
In this article I will try to easily explain the principles and the preparation process but this is not intended to be considered as a replacement of the official books. My intention is only to provide you with an easy and quick reference mainly for the process FMEA.
FMEA Types
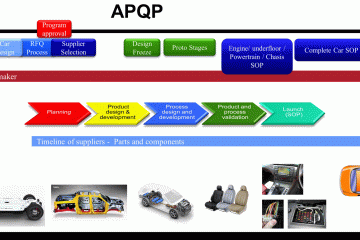
Design FMEA. This FMEA is used to cover the product and its conception process. It covers risks related to dimensions, materials, tolerances, colors, interactions with other components or systems and every other characteristic which could affect the product conformity to the specifications, expectations and/or regulations, or overall performance and product life. The DFMEA is normally made by an interdisciplinary team during the Product Design and Development phase of the APQP (you can read the post APQP – Quick Reference).
Process FMEA. It is made to prevent and treat risks that can potentially appear in the realization process of the product. Factors to consider are materials, components, material flow, machines, people, process parameters, methods, measurement systems, tools, procedures, handling, etc. The DFMEA is normally used as input when preparing and reviewing the PFMEA because it summarizes requirements, possible failures modes, causes and consequences related to the product.
Machine FMEA. As of today is not yet a customer requirement but this FMEA focuses on preventing and treating risks related to the performance and functionality of machines, tools and equipment.
FMEA form.
As any other risk management technique, the main function of the FMEA is to prevent and/or to address risks. The risk is a potential failure which can appear due to certain causes and have negative consequences or effects.
A failure mode is the way in which a problem may appear and can manifest as a non-conformity to the specification and/or the expected function.
The effects are the negative impacts of the failure for the final customer, internal customers (subsequent processes) or the organization.
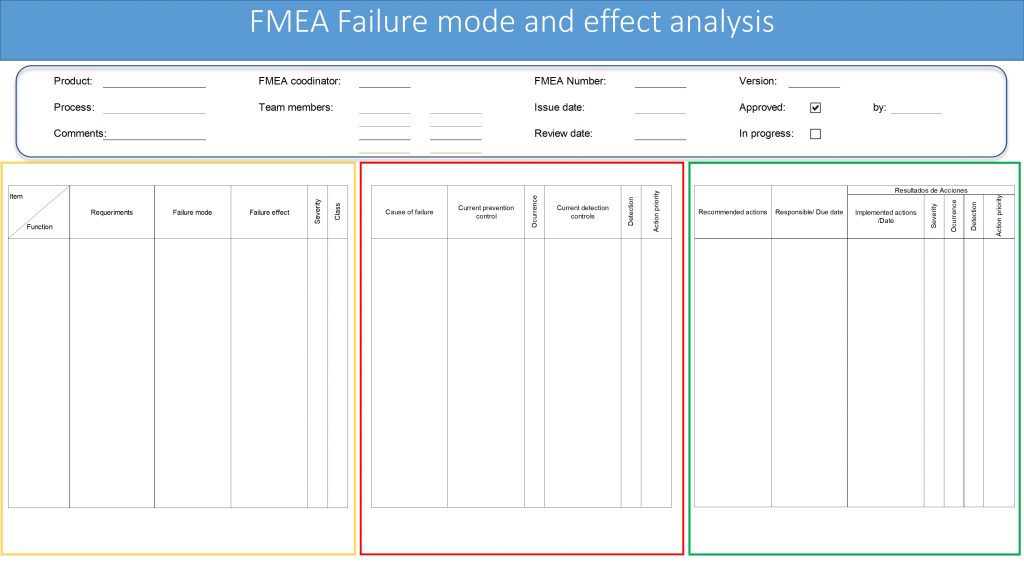
If we compare the following FMEA Form to other risk management techniques, we will find in the summary form, 2 important sections:
- Analysis. Take a look at the image. It covers the blocks in yellow and red.
- Risk treatment. Take a look at the green section.
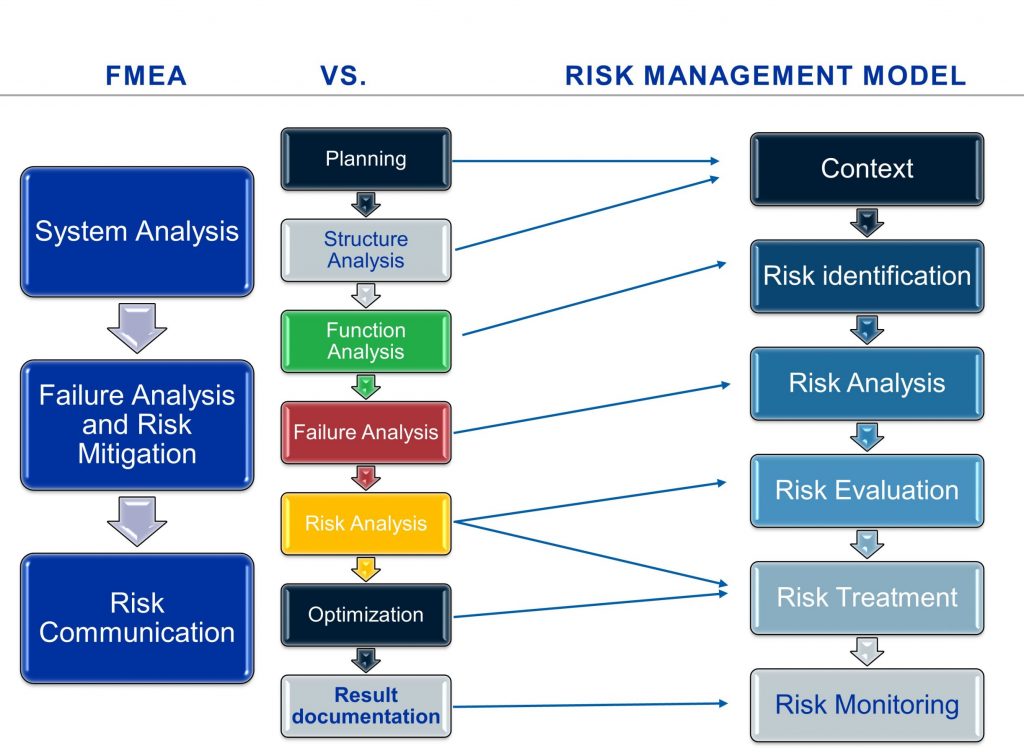
FMEA Seven Steps
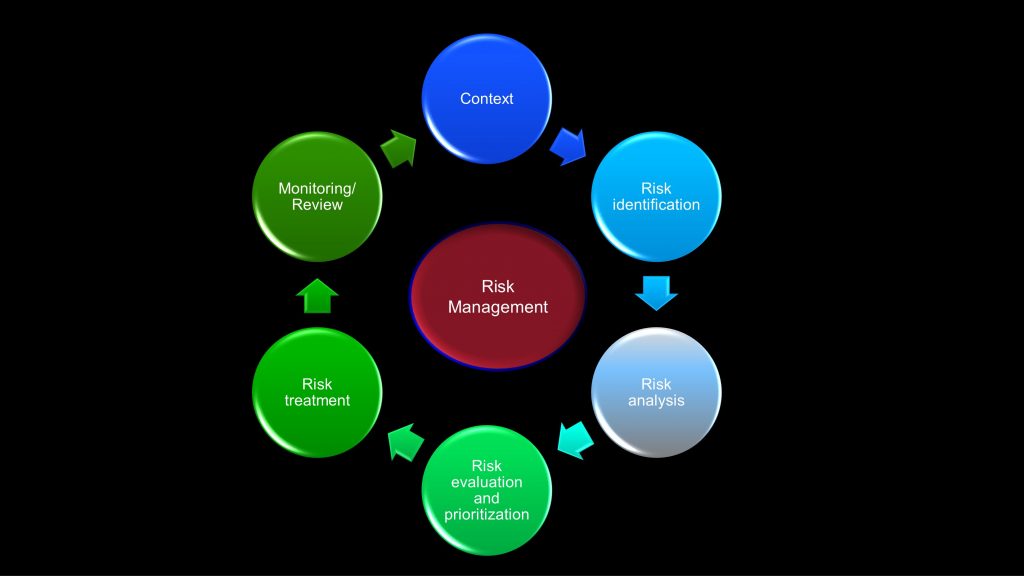
If you know the basics of risk management you might remember the overall structure that you can also see in the next image.
Quick reference
The seven steps are grouped in three sections:
System Analysis
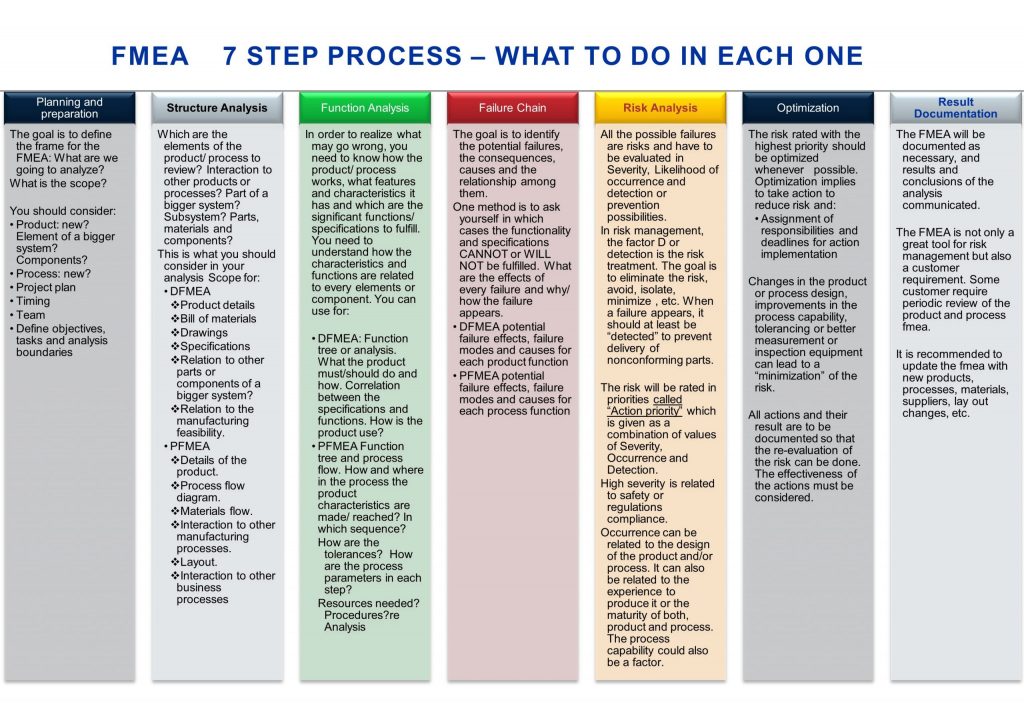
- Planning. The first step is the planning where the project is defined and the reach of the analysis is described. The product must be the base and what will be included and excluded must be determined here. Timeline, objectives, leader and multidisciplinary team, taks, etc. will be established.
- Structure Analysis. The product/process to be analyzed is part of a system and also has components, materials, dimensions, tolerances, etc. For the DFMEA you need drawings, bill of materials, explosive views, 3D models, connectivity or interaction to other parts or systems, etc. For the PFMEA you need data of the product but also know how the manufacturing process will be and you need process flow, materials flow, machines details, etc.
- Function analysis. Exactly like the overall risk management process, the FMEA is done in sequence. You must have the first step to move to the second and so on. Once you know details of the product you can correlate those details to the expected functions and performance. In the PFMEA, you need to know goal and function of every process step.
Failure analysis and risk mitigation
- Failure analysis. What can go wrong? which are the consequences? what are the causes? How severe can the problem be? How often can it happen? What is the probability that it happens? You need to link the failure mode with the effects and causes.
- Risk analysis. This step is like the evaluation and prioritization in risk management. In the FMEA process, here the risks will be evaluated with the Severity, likelihood of Occurrence and possibilities to prevent it from happening or to detect or to control the impact if occurs. Based on these factors, all the possible failures will be ranked and prioritized. At the end of the article you will find the VDA/AIAG evaluation tables for the PFMEA including the Action priority table. As reminder:
- Severity: How bad are the consequences of the failure for the final or internal customer.
- Likelihood of occurrence. How probable is it to happen? How often can it happen?
- Prevention/ Detection. How easy is to prevent it from happening? How easy is to detect it or to control it once it has happened?
- The combination of the three factors give the AP Action priority. the worse the risk, the higher the priority to treat it. H= High, M= Medium, L=Low.
- Optimization. One important part of the previous step is also the risk treatment as “prevention” or “detection”. However, for certain risks, you can modify the design, improve technology, acquire a better inspection/ detection or prevention system, etc. These actions may lead to new values of priority and therefore you should record them, assign for implementation and evaluate their effectiveness.
Risk Communication
- Results and communication. The form shown above can be considered as one of the final documents where the process is documented. In this phase a summary of the process with the scope, action priority list and conclusions are officially documented. Many customers require regular reviews to the FMEA to guarantee that it remains up-to-date and effective.
Do you need a summary form?
Please always think about the official handbook of the VDA/AIAG and your customer requirements before using any other documents. There are also many companies which offer software for the preparation of FMEA and control plan. As a quick and easy reference, i have also prepared some documents for you. Feel free to read them, download and use.
Regards, Miguel.
PFMEA 7 Steps
Severity, Occurrence, Detection matrix
Action priority table
FMEA Form
What about an excel form?
The file was made for one of my training sessions. It is based on the VDA/FMEA manual and gives you the Action priority ratings once you have entered the data and values S-O-D. The last page is the control plan form. Take a look first and if you like it, click on the image below.

0 Comments