APQP
The first thing to know about the APQP is that it is a project management tool. APQP stands for Advanced Product Quality Planning and it is widely used in the automotive industry. It was published with the blue books (manuals of the AIAG) when the QS9000 was the quality standard for Quality Management Systems.
In the QS9000 there were requirements based on the ISO9001:1994 but there were also automotive requirements from the big three: GM, Ford and Chrysler. The APQP was ever since, required as project management tool.
Project management
So, let’s start with the basics of project management:
Project:
A project is a temporary endeavor to produce a unique product, service or result under given conditions, constrains or rules and with a defined beginning and end. Time, budget and scope are normally some of those constraints.

Project types:
Think of a product, service or task and every one of them can be a project. I could even say that the project type is directly related with the intended use of the product or service.
Construction, investments, software development and even a hobby can be managed as projects.
Project management:
- Project management is the tool we use to lead the work in order to achieve the goals in the right time, budget, etc.
Depending on the type of project, the management style may vary but in general the project management has the following structure:
- Initiation.
- Planning.
- Executing.
- Monitoring and controlling.
- Closing.

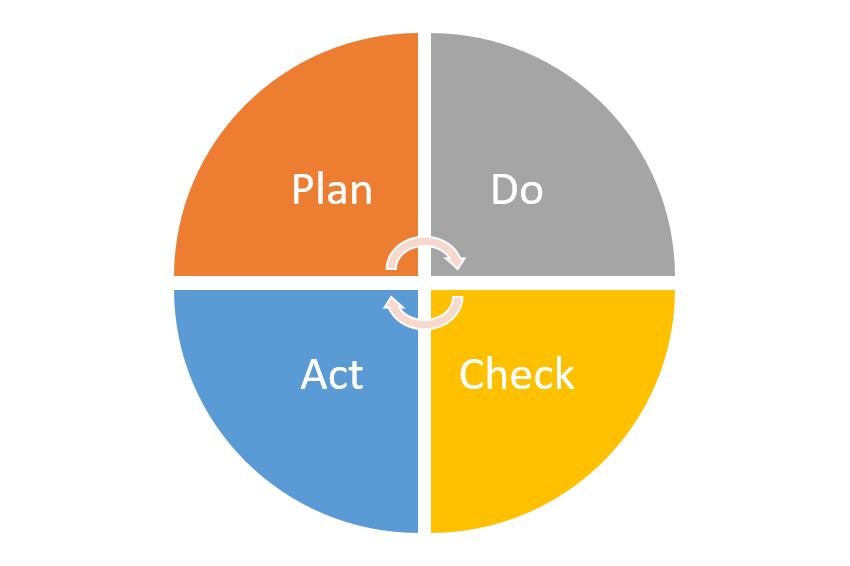
PDCA
Depending on the project, the execution could/must/should be made in steps, phases or iterations. In every one of them there is a review, evaluation, correction, etc. The PDCA cycle might be applied several times during the life of a project.
This needs to be considered as well in the APQP structure.
Imagine a construction project, for example a house. It will be gradually built. The base, the structure, pipes, etc., must be made or installed in the right sequence. But, if there is a problem in the process, parts or components affected must be corrected, repaired or removed/replaced as many times as needed until the overall task/ stage is ok and you can move to the next.
What makes the APQP so unique?
Automotive industry.
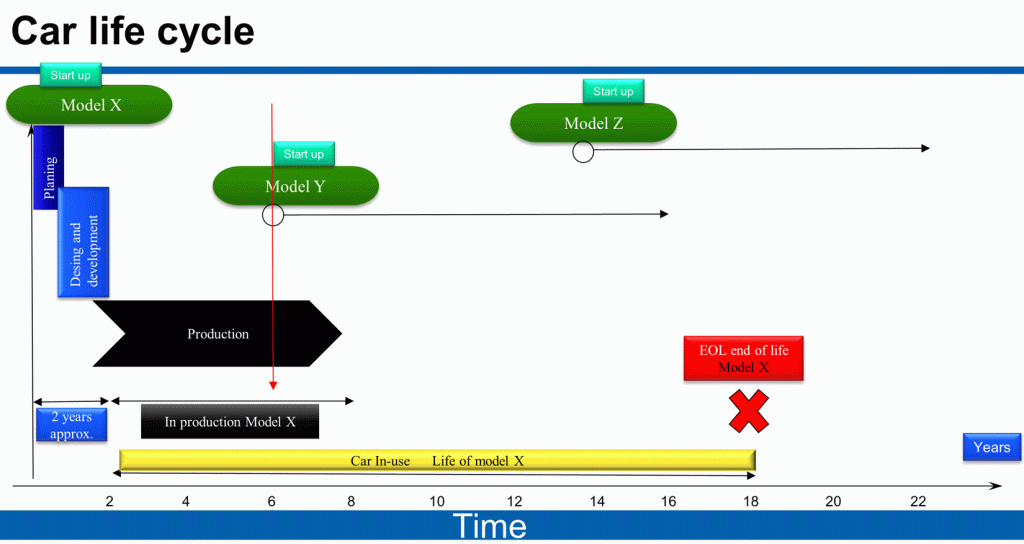
Product life-cycle.
The automotive industry is in constant change. Cars are produced for a period of time and then replaced for a more modern version. On the next image you can find an example: The company Fenix produces cars, every 4-6 years it launches a successor of his most famous car. While Model X is in serial production, the Model Y is in development. A little after the Model Y has been launched, the planning of the Model Z starts.
APQP is also important because it makes you include all the Core Tools into the development process and therefore you will see elements like FMEA (failure mode and effect analysis), Control Plan, MSA (Measurement System Analysis), SPC (Statistical Process Control) and PPAP (Production Part Approval Process) in all APQP projects.
And of course, in the automotive industry there are many safety-related systems and components which must be developed with the best techniques and concepts in order to minimize the risk of failures. Safety is extremely important.
As you might remember, one of the best quality assurance techniques is prevention. If the product and the corresponding manufacturing process are well designed, tested and validated prior to SOP (Start of Production), we will prevent failures.
I personally consider the following points as the drivers of the APQP process:
- Conformity of product and customer satisfaction.
- Focus on safety and error prevention.
- Reduced development time.
- Warranty, recall and claim prevention.
- Base and reference for the serial production.
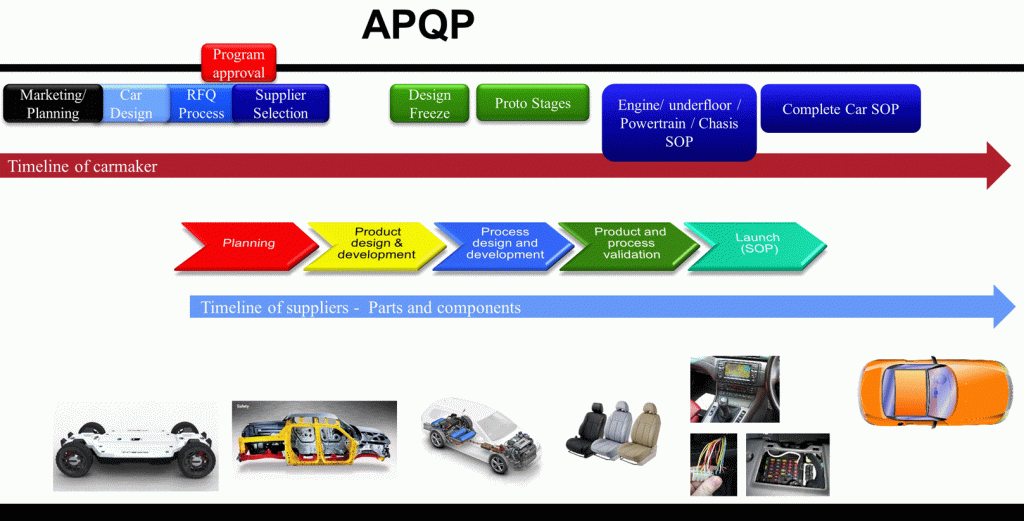
APQP Phases
For the autopart suppliers, the APQP process starts with the nomination of the project (letter of intention or purchase order) even when prior to this there might have been activities with or without impact to the project.
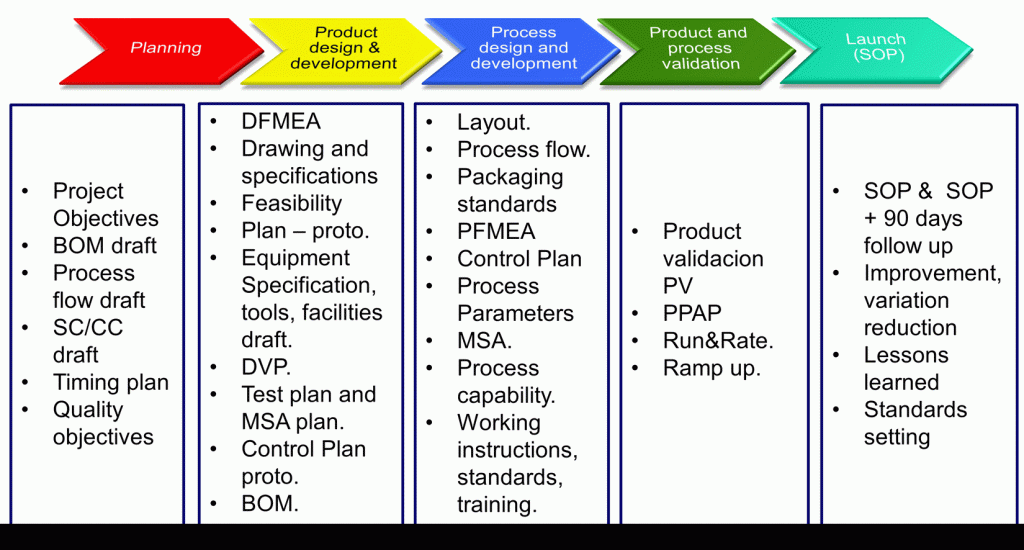
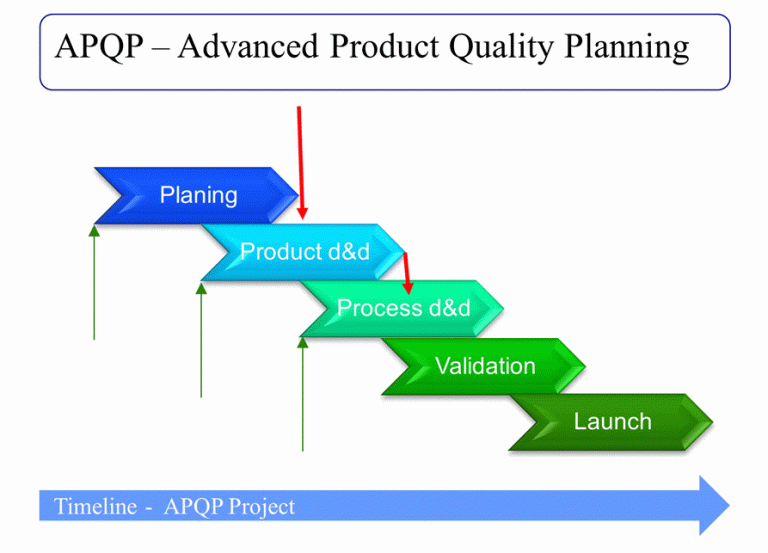
There are five phases in an APQP project:
- Planning. This is the organization of the project. Leader and team members must be named, resources provided, constraints, goals and objectives identified. The timeline must be set and the milestones defined. Risk, opportunities and lessons learned from prior projects must be considered and quality targets set.
- Product Design and Development. The product is conceived and all technical data is prepared like drawings, 3D models, bill of materials, product and material specifications, SC/CC, Tolerancing. The functionality must be tested and the design validated DVP (Design Validation Plan). Design FMEA and impact in Process FMEA, Process capability, MSA should be considered during the product design.
- Process Design and Development. Here, the goal is to prepare everything needed for the serial production like final process definition, parameters, material flow, plant layout, maintenance plans, control plan, procedures, working instructions, training plan, etc.
- Product and Process Validation. The product/process must fulfill all specifications and functionality. This can be made confirmed with the test and measurement results of the DVP and the PV (Product Validation). Purchased parts, materials and components must be validated (ppap’ed), process capability and measurement capability must be confirmed. PPAP must be prepared.
- Launch. PPAP must be approved. The first deliveries in bigger quantities must be made and the production capacity confirmed during a “run @ rate” (produced pieces/ time). The SOP takes place and the product, service, quality, customer feedback must be tracked during ~90 days to confirm the “safe launch”. In case of problems, they must be solved.
As quick reference:
But please note that not all deliverables (inputs /outputs) are shown. If you need more details, please take a look at the AIAG APQP manual and/or the VDA RGA manual (Reifegradabsicherung -maturity model, often required for German customers-).
Just keep in mind...
In a real project, you will see often that there is not a 100% transition from the first stage to the second and so on. Normally there is an overlap between phases. It can also happen that one element must be corrected or changed several times and becomes critical.
This means that some tasks may require more time or resources due to their complexity and could extend into the next phase. In other cases, activities of two different phases can be started at the same time or simply have a shorter duration than planned. The project manager and the team can and should adjust the plan as needed.
Steering committee and Escalation process.
If you go back to the overall project management definition you will note that one of the phases is Monitoring and Controlling.
In the project structure there are normally elements or tasks to monitor and to control the quality. The project manager, has the responsibility to take action when needed to solve problems. Depending on the severity and complexity of the problem, there might be an escalation process.
This means that in the project plan there should be a procedure or process to identify problems and to manage them. When a task, element or deliverable goes wrong, the team must react and solve it to avoid major delays which would endanger the success of the project. Some companies use traffic light colors like green, yellow and red to evaluate the risks or problems in every stage of the project. The sooner the team reacts, the better.
When the conformity of the product and/or the SOP become uncertain, delayed or somehow endangered it is too late. Reasons for this can be that the project team missed or ignored the problems or performance indicators, lacked of knowledge, skills or resources and failed to follow the escalation process. Of course nothing is 100% sure but with the right planning and execution, most of problems can be avoided. When the team cannot longer manage or solve the problem within the scope, constraints and resources, they need to ask for support from the top management.
In project management there is always one person or a team of people who have enough authority, responsibility and interest (stakeholders) to steer the project in a high level: The steering champion or steering committee.
This committee has the right, power and obligation to support the project leader and the team, especially when problems arise and go beyond a certain level. The committee can also help to ensure that all the resources needed are available, give approvals, change or modify the scope of the project, increase the budget, etc.
In the automotive industry this steering committee should, at least include one top manager. Some customers like GM and Ford require the signature of the plant manager in many project documents as guarantee that he was informed and has approved the phases of the project. This is called gate closure. Each phase of the APQP must be reviewed and signed-off by the steering committee. The idea is to make sure that the top managers are aware of the project status and make the right decisions in the right time in case of problems.
Project manager and communication
The project manager must be not only skilled in project management techniques but has to be a good communicator and motivate the team to work at their best potential. He needs to react in a timely manner when needed. He has to be a leader.
One of my managers used to say:
A project manager who identifies and escalates a problem is good but the project manager who prevents problems or solves them before they “escalate” is the type of person I need.
The project manager must be a link between the steering committee and the project team and of course communicate horizontally with all the team members.

0 Comments